Hospital Heated Air Blankets, also known as warming blankets or forced-air warming systems, are a common sight in hospitals and medical facilities. These specialized blankets play a crucial role in regulating body temperature and enhancing patient comfort during various medical procedures and recovery periods. But how exactly do these blankets work and what are the benefits of using them?
Understanding Hospital Heated Air Blankets
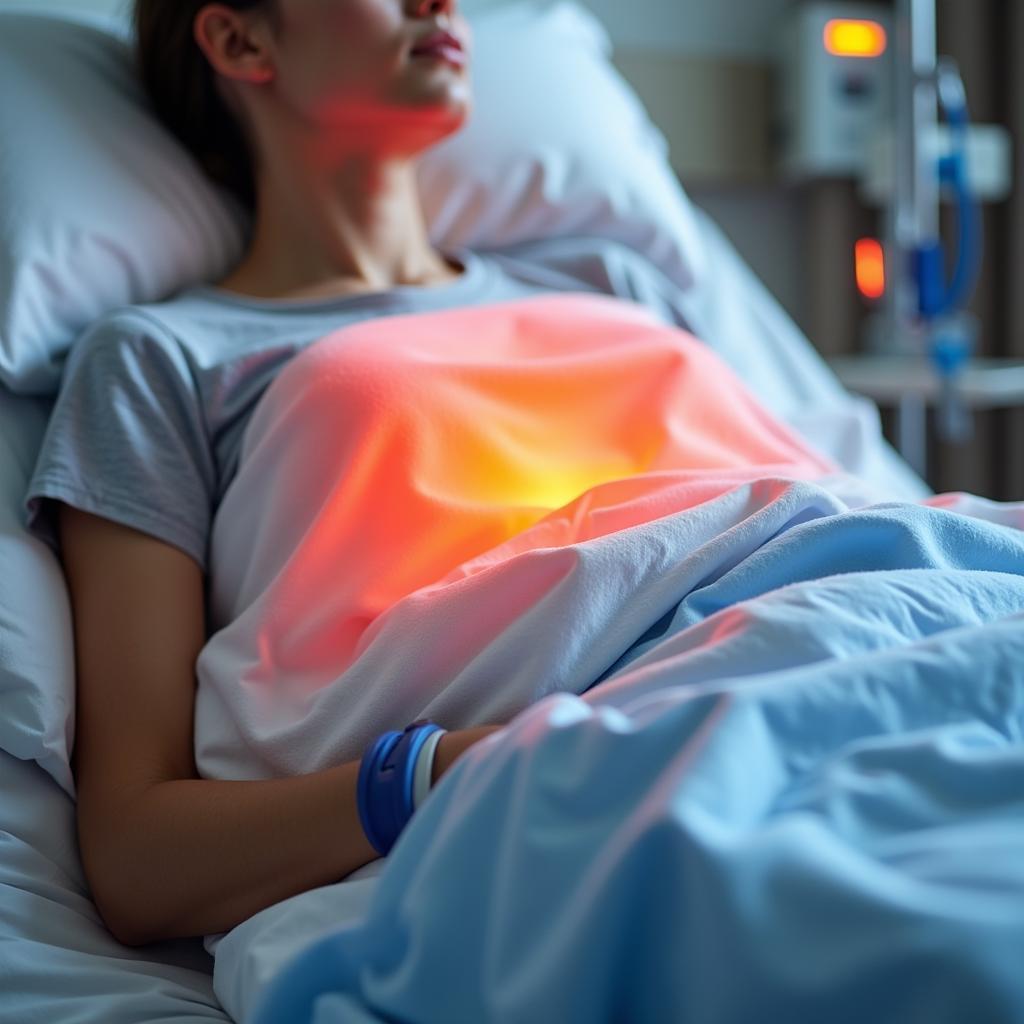 Patient using a hospital heated air blanket
Patient using a hospital heated air blanket
Unlike traditional blankets that provide insulation, hospital heated air blankets use warm air circulation to maintain a patient’s body temperature. The blanket itself is made of a lightweight material that allows warm air to pass through tiny holes. This warm air is generated by a separate unit and delivered through a flexible hose connected to the blanket.
The Benefits of Hospital Heated Air Blankets
Hospital heated air blankets offer numerous benefits for both patients and medical professionals:
- Maintaining Normothermia: One of the primary functions of these blankets is to prevent hypothermia, a condition where the body’s temperature drops below 95°F (35°C). Hypothermia can lead to various complications, especially during and after surgery.
- Improved Comfort: The gentle warmth provided by these blankets helps patients feel more comfortable and relaxed, particularly those experiencing chills or discomfort due to medical conditions or treatments.
- Faster Recovery: Studies have shown that maintaining a stable body temperature can promote faster healing and recovery after surgery or illness.
- Reduced Risk of Infection: By keeping patients warm, heated air blankets help minimize the risk of surgical site infections.
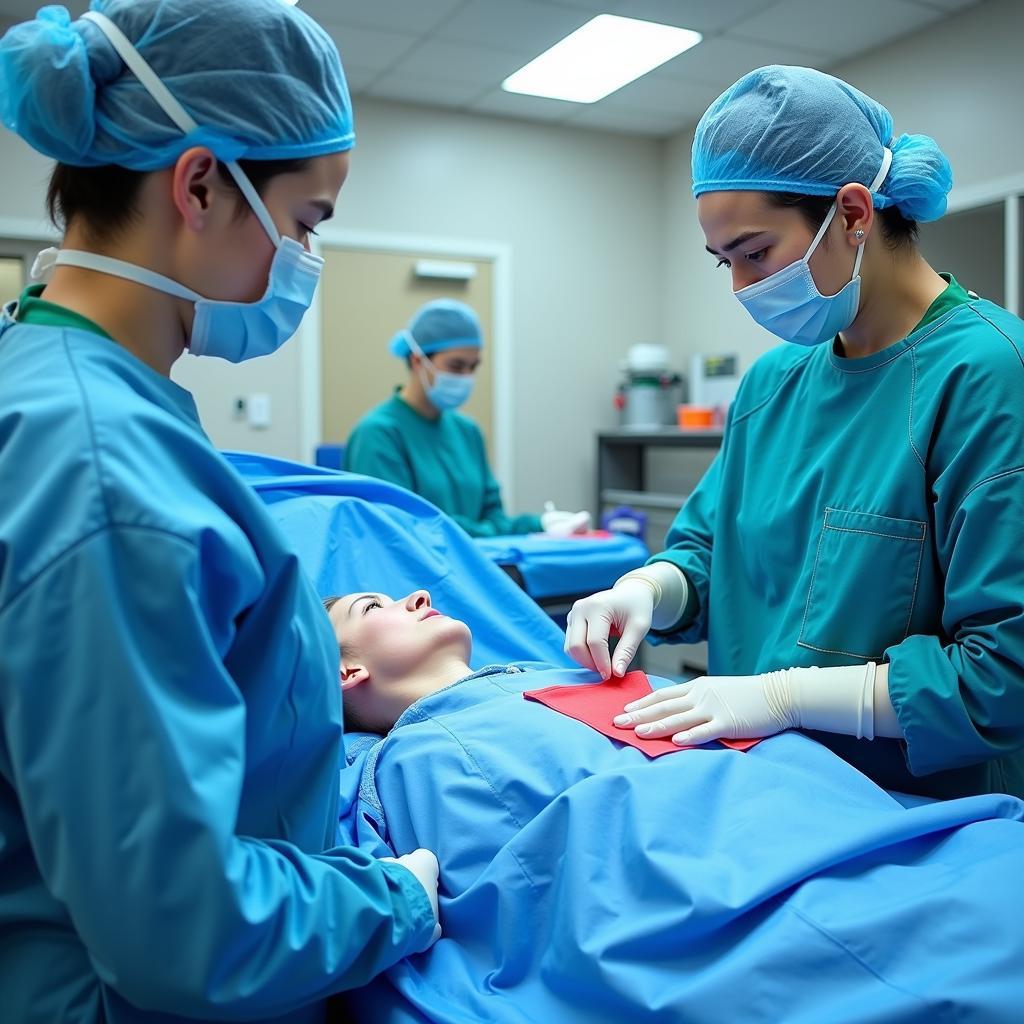 Hospital heated air blanket in a surgical setting
Hospital heated air blanket in a surgical setting
How are Hospital Heated Air Blankets Used?
Hospital heated air blankets are used in various medical settings and situations:
- During Surgery: These blankets are commonly used during surgical procedures to counteract the effects of anesthesia and cold operating room temperatures, which can lower body temperature.
- Post-Surgery Recovery: After surgery, patients are often moved to a recovery area where heated air blankets are used to help them regain a normal body temperature and prevent shivering.
- Emergency Room Care: Patients arriving in the emergency room with hypothermia or at risk of developing it, such as those exposed to cold weather, may benefit from the use of these blankets.
- Intensive Care Units (ICUs): Critically ill patients in ICUs often require careful temperature regulation, and heated air blankets can be a valuable tool for achieving this.
Choosing the Right Hospital Heated Air Blanket
There are different types of hospital heated air blankets available, each designed for specific purposes:
- Reusable Blankets: These blankets are designed for multiple uses and are typically made of durable materials that can withstand repeated cleaning and sterilization.
- Disposable Blankets: Single-use blankets are often preferred in settings where infection control is paramount, such as operating rooms.
- Bariatric Blankets: Larger blankets are available to accommodate the needs of bariatric patients.
 Different types of hospital heated air blankets
Different types of hospital heated air blankets
Safety and Precautions
While hospital heated air blankets are generally safe, it’s important to use them correctly to avoid potential risks:
- Burns: Always ensure the blanket’s temperature is set at a safe level to prevent burns, especially for patients with sensitive skin or reduced sensation.
- Electrical Safety: Regularly inspect the blanket and its cords for any damage, and do not use a damaged blanket.
- Proper Positioning: Make sure the blanket is positioned correctly on the patient to avoid wrinkles or bunching, which can impede air circulation and increase the risk of burns.
Conclusion
Hospital heated air blankets are an essential tool in healthcare settings, playing a vital role in maintaining patient comfort and well-being. By understanding the benefits, uses, and safety precautions associated with these blankets, medical professionals can ensure their effective and safe use to optimize patient care and recovery.